Inpatient Care for Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a common respiratory infection that affects individuals outside of healthcare facilities. When managing CAP, inpatient care plays a crucial role in ensuring patient recovery. Let’s explore the key aspects of inpatient management for CAP.
1. Diagnosis and Severity Assessment
- Clinical Evaluation: Physicians assess symptoms, perform physical examinations, and order diagnostic tests (such as chest X-rays and blood cultures) to confirm CAP.
- Severity Scoring: Tools like the CURB-65 score help determine the severity of pneumonia and guide treatment decisions.
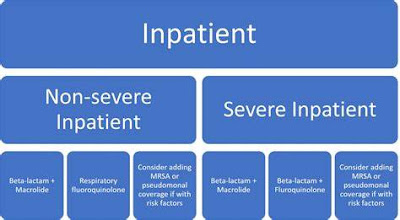
2. Antibiotic Therapy
- Empirical Treatment: Start empiric antibiotic therapy promptly based on severity and risk factors.
- Guidelines: Follow evidence-based guidelines (e.g., IDSA/ATS guidelines) for selecting appropriate antibiotics.
3. Supportive Measures
- Oxygen Therapy: Administer supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen saturation.
- Fluid Management: Ensure proper hydration.
- Pain Control: Manage pain and discomfort.
4. Monitoring and Response Assessment
- Clinical Monitoring: Regular assessments of vital signs, oxygen saturation, and mental status.
- Response to Treatment: Evaluate improvement or deterioration.
5. Discharge Planning
- Criteria for Discharge: Patients should meet specific criteria (e.g., stable vital signs, ability to tolerate oral intake) before discharge.
- Follow-Up: Arrange follow-up appointments and provide clear instructions for home care.
Remember, personalized care is essential. Consult with a healthcare provider for individualized recommendations.